Unraveling the Mystery of Plasmid DNA: From Our Food to Vaccines
Plasmids are like nature's tiny USB sticks, except they store genetic information instead of storing your holiday photos. They're doing some pretty wild things in our world today, and you've probably heard whispers about plasmid DNA being in everything from our food to vaccines. Sounds like science fiction, right? Buckle up, because we're about to dive deep into the curious case of these microscopic rings of DNA, and by the end, you'll be schooling your friends on genetics like a pro.
Content List
- Introduction
- What is Plasmid DNA?
- Plasmids in Bacteria: Nature's Little Hackers
- How Do Plasmids End Up in Our Food?
- Water and Air: Vehicles for Plasmids?
- Plasmid DNA and Vaccines: What's the Deal?
- Why is Plasmid DNA Relevant to Me?
- Could Plasmids Improve Our Health?
- The Risks: When Plasmids Go Rogue
- The Future of Plasmids in Science
- How Can We Protect Ourselves?
- A Word of Caution from TrueHealing: The Risks of Rushing into Genetic Technologies

What is Plasmid DNA?
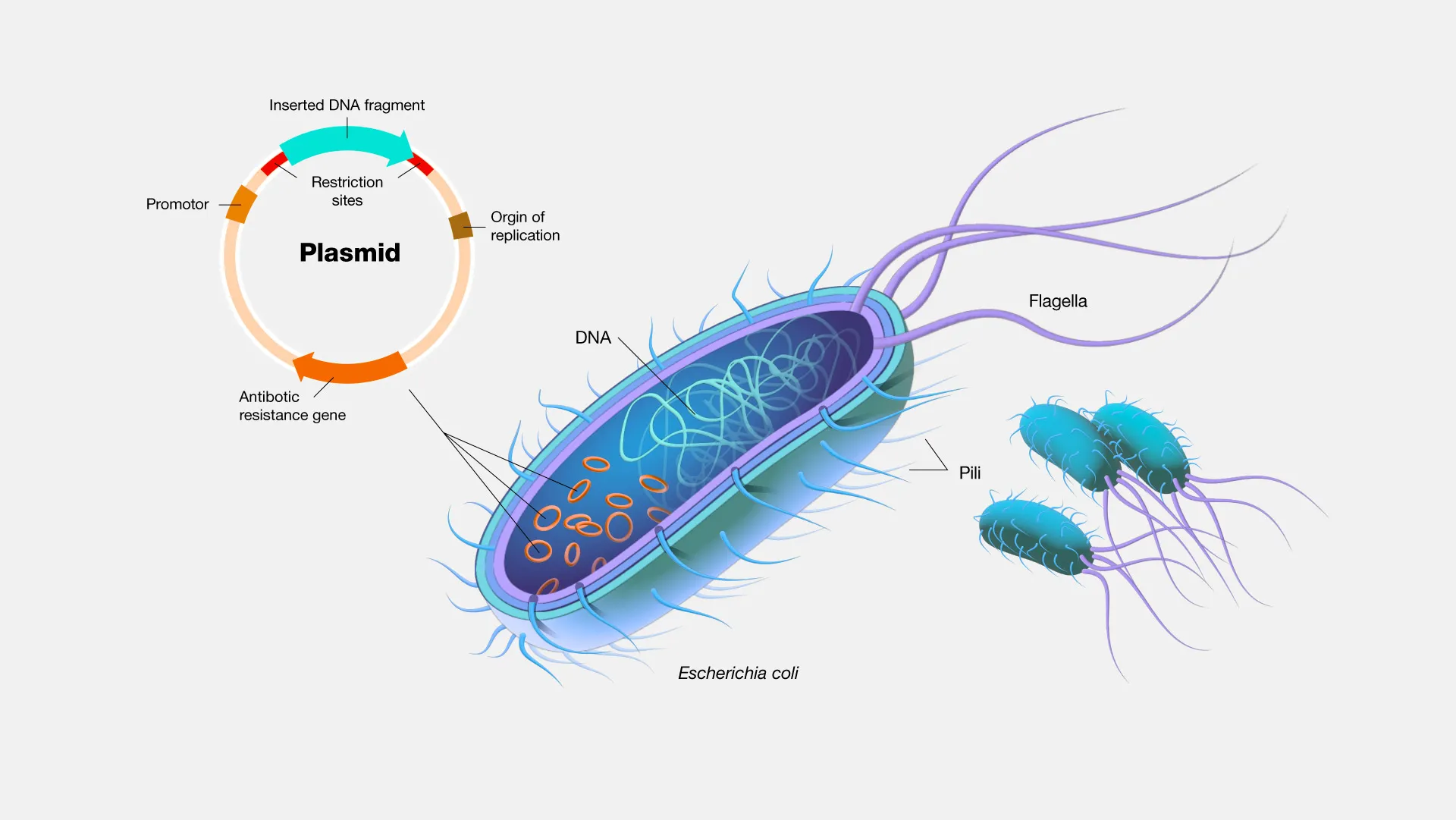
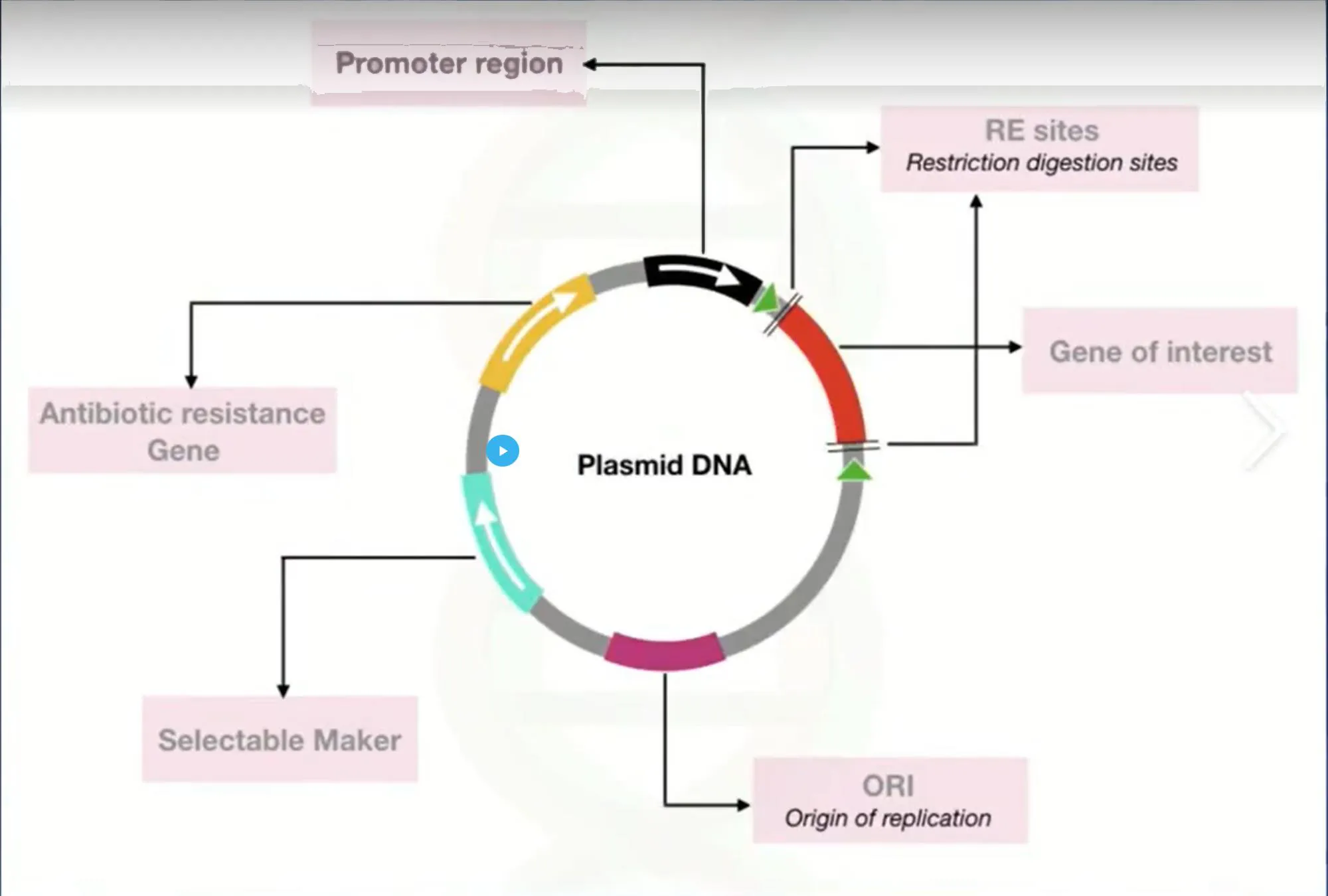
Plasmid DNA is like the wild card in the deck of life. These are small, circular pieces of DNA that can replicate independently of the chromosomes within cells. Imagine them as tiny life-forms, doing their business inside bacterial cells, occasionally jumping ship to other cells, and shaking things up with their genetic data. Plasmids are fascinating genetic entities that have the potential to influence various aspects of life, from agriculture to medicine, making them a subject of great interest and importance in the scientific community.
Plasmids in Bacteria: Nature's Little Hackers
In the microbial world, plasmids are like cheat codes for bacteria, allowing them to gain superpowers like antibiotic resistance or the ability to metabolize toxic waste as if it were candy. These circular DNA molecules act as little genetic freeloaders, hitching rides in bacteria and sometimes even getting swapped around like Pokémon cards in a playground. Understanding the role of plasmids in bacteria sheds light on the intricate mechanisms that drive genetic adaptation and survival in microbial communities, offering insights into the potential risks and benefits associated with their presence.
How Do Plasmids End Up in Our Food?
Yup, you heard that right. Plasmids in our munchies. It's not like someone's sprinkling them on like seasoning, but they do get into crops through genetic engineering. Scientists insert beneficial plasmids into plants to help them resist pests or grow faster. So, when you bite into a genetically modified (GM) tomato, you're also getting a taste of plasmid action. This process of genetic modification in agriculture has raised concerns and sparked debates about the implications of introducing engineered plasmids into the food chain, prompting discussions about the potential long-term effects on human health and the environment.
Water and Air: Vehicles for Plasmids?
Here's a crazy thought: plasmids can travel through water and air. These tiny genetic stowaways can move through the environment, and some fear that they could spread antibiotic resistance widely. It's like a ninja smoke bomb but with DNA. The ability of plasmids to traverse environmental mediums raises questions about the potential for widespread dissemination of genetic traits, particularly those associated with antibiotic resistance, highlighting the need for comprehensive strategies to mitigate the risks posed by the mobility of plasmid DNA.
Plasmid DNA and Vaccines: What's the Deal?
When it comes to vaccines, plasmid DNA is a hot topic. They're used as a starting point in creating some vaccines, like the COVID-19 jabs. The idea is to give the immune system a sneak peek at the enemy so it's ready to fight when the real baddies appear. The utilization of plasmid DNA in vaccine development underscores the innovative approaches in immunology, offering insights into the potential for harnessing genetic elements to induce protective immune responses against infectious diseases, paving the way for advancements in vaccine technology.

Why is Plasmid DNA Relevant to Me?
If you're scratching your head wondering why you should care about these microscopic loops of genes, here's the deal: plasmids are changing the game in health, agriculture, and the environment. They're the unsung heroes (and sometimes villains) in the story of life on Earth. Understanding the relevance of plasmid DNA in various aspects of life underscores the need for public awareness and informed decision-making regarding the implications of genetic technologies, emphasizing the importance of engaging in discussions about the ethical, social, and environmental dimensions of genetic advancements.
Could Plasmids Improve Our Health?
Scientists are exploring how plasmids can be used to treat diseases, not just cause them. We're talking gene therapy, where plasmids become the FedEx of the body, delivering healing genes to where they're needed most. It's like a biological patch-up kit. The potential for plasmids to serve as vehicles for gene therapy highlights the transformative potential of genetic technologies in healthcare, offering prospects for targeted and personalized approaches to treating genetic disorders and chronic diseases, paving the way for advancements in precision medicine and therapeutic interventions.
The Risks: When Plasmids Go Rogue
Here's the flip side: when plasmids spread traits like antibiotic resistance, it's like they're creating superbugs on steroids. It's one of those "with great power comes great responsibility" scenarios, and sometimes, things can go pear-shaped. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria due to the dissemination of plasmid-borne resistance genes underscores the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to mitigate the risks posed by the spread of genetic traits, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship and surveillance in managing the impact of plasmid DNA on public health and the environment.
The Future of Plasmids in Science
The potential for plasmids in biotechnology is huge. We could see plasmids being used to clean up oil spills, produce biofuel, or even create new medicines. The future could be bright as long as we handle these biological tools with care. The prospects for leveraging plasmids in biotechnological applications underscore the transformative potential of genetic technologies in addressing pressing global challenges, offering avenues for sustainable solutions in environmental remediation, renewable energy production, and pharmaceutical innovation, paving the way for advancements in biotechnology and bioengineering.
How Can We Protect Ourselves?
With all this genetic wizardry happening, you might wonder how to stay safe. It's all about being informed, understanding the science, and making conscious choices about what we eat and the treatments we choose. The imperative of informed decision-making and public engagement in discussions about genetic advancements underscores the need for proactive measures to promote scientific literacy, ethical considerations, and regulatory frameworks, emphasizing the importance of fostering a culture of responsible innovation and governance in the realm of genetic technologies.
A Word of Caution from TrueHealing: The Risks of Rushing into Genetic Technologies
Amidst the whirlwind of genetic advancements and the groundbreaking uses of plasmid DNA in our everyday lives, we at TrueHealing advocate for a moment of reflection and prudent consideration. The implementation of plasmid technology, particularly in fields as impactful as our food supply and medical treatments, is not to be taken lightly.
The recent experiences with the COVID-19 vaccine rollout provide a poignant example. The speed at which these vaccines were developed, while a testament to human ingenuity and determination, also left many questions unanswered—questions that pertain to long-term consequences and the full spectrum of potential side effects.
At TrueHealing, our skepticism stems from a place of genuine concern. We believe that the long-term effects of using plasmid DNA technology are not sufficiently researched and that the public's knowledge about their exposure to such technologies is often limited or non-existent. Individuals may not realize that the genetically modified foods they consume or the vaccines they receive involve the transfer of plasmid DNA, which could have implications that extend far beyond current scientific understanding.
In a nutshell:
- Plasmid DNA is part of the genetic material found in cells, especially bacteria.
- Through genetic engineering, plasmids are used in agriculture to enhance food production.
- There's some concern about the spread of antibiotic resistance via plasmids.
- Vaccines utilize plasmid DNA technology to develop harmless mimicry of pathogens to induce immunity.
- While plasmids offer exciting possibilities in biotech, we must tread carefully to avoid unintended consequences.
The summary encapsulates the multifaceted role of plasmid DNA in shaping various aspects of life, underscoring the need for comprehensive approaches to harness the potential benefits of genetic technologies while mitigating the associated risks, emphasizing the importance of responsible stewardship and governance in the realm of genetic advancements.
Reference:
Dr Bryan Ardis - Man in America Podcast
Dr. Bryan Ardis is a retired chiropractor and acupuncturist who deeply believes in nature's healing power. Dr. Ardis founded two healing centers, one in Tennessee and another in Texas, which he later sold. He now focuses on ArdisLabs LLC and hosts 'The Dr. Ardis Show,' advocating for natural health solutions.