Unveiling the Secrets of the Human Microbiome: The Hidden World Within Us
Discover the intricate world of the human microbiome, the diverse community of microorganisms living inside your body. This article promises enlightening insights into how these tiny inhabitants affect your overall health and contribute to your everyday life. Here's why you must dive into the wonder of your inner ecosystem.
Content
- What is the Human Microbiome?
- Who Are the Inhabitants of Our Inner World?
- How Does the Microbiome Impact Our Health?
- Can Our Microbiome Influence Brain Function?
- What Makes Our Microbiomes Unique?
- How Does Diet Affect Our Microbial Partners?
- The Threat of Antibiotics to Microbial Diversity
- What Can We Learn From Microbiome Research Advancements?
- The Future of Microbiome-Based Therapies
- Conclusion: The Microbiome's Influence and the Path Ahead

1. What is the Human Microbiome?
The human microbiome signifies a vast ensemble of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other tiny life forms that dwell in and on the human body. When we speak of gut microbiota or gut microbiome, we're referring to the microbial communities that reside within our gastrointestinal tract, where they perform a myriad of functions essential for our health. These microbial inhabitants are more than just occasional visitors; they constitute an integral part of who we are, engaging in a symbiotic relationship with their host — us.
2. Who Are the Inhabitants of Our Inner World?
Our bodies are bustling ecosystems, home to various microbial life, each housing an assortment of beneficial bacteria, opportunistic commensals, and potential pathogens. This vibrant collection of microorganisms makes up our gut microbiota and extends to various parts of our body, each with its unique microbial communities. The gut microbiome, in particular, stands out in its microbial density and diversity, teeming with countless microbe varieties that contribute to our well-being.
The microbial species making up these communities are not static; they are influenced by many factors, including our genetic makeup, the environments we interact with, and the foods we eat. The ecology of our microbiome may shift with lifestyle changes, diet modifications, and even as we journey through different life stages. Research has shown that the microbial composition of our gut microbiota continues to evolve from birth to old age, underscoring the dynamic nature of these organisms.
Probiotics, which comprise beneficial bacteria administered to improve gut health, highlight the positive effects that certain microbes can have on our bodies. Meanwhile, studies have shown that other microbial species can influence the onset of health and disease, suggesting that the balance of our internal microbiota has far-reaching implications for human health and disease. Therefore, understanding and maintaining this delicate balance of gut microbes is paramount for promoting a healthy human body, home to this complex and ever-changing array of microorganisms.
3. How Does the Microbiome Impact Our Health?
The impact of the microbiome on our health is both wide-ranging and profound. Our human gut is the epicenter of this complex ecosystem. These housing trillions of microorganisms play an indispensable role in digestion, breaking down food, and aiding in absorbing essential nutrients. However the influence of these microorganisms extends far beyond the digestive tract. They are deeply intertwined with the metabolic pathways of the human body, contributing to the metabolism of drugs, detoxification processes, and energy extraction from the diet.
The microbiome is also a central component of our immune function. These microscopic entities educate our immune system, helping to distinguish between friendly and harmful invaders, which is paramount for our survival. The human body is home to this intricate network that is constantly communicating with our physiological systems, maintaining a balance that keeps us healthy.
The gut microbiome has been implicated in a variety of neurological functions. Research has revealed a bidirectional communication network, often called the gut-brain axis, through which the microbiome can influence mood, stress responses, and even cognitive abilities. As we delve deeper into microbiome research, we continue to discover how these microscopic inhabitants can bolster our defenses and potentially contribute to various health conditions, highlighting their dual role in protecting and impacting human health.
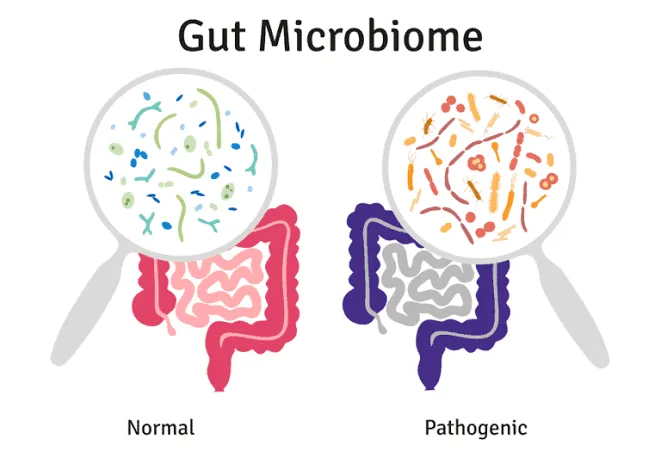
4. Can Our Microbiome Influence Brain Function?
Compelling research suggests a communication pathway between the gut and the brain. Microbes in our gut can produce neurotransmitters and other chemicals that may influence brain function, affecting our behavior and emotions. Additionally, the gut microbiota has been found to play a role in the development of the central nervous system and in the regulation of stress and anxiety. Studies have shown that the composition of the gut microbiota can impact brain function and mental health, with alterations in the microbiome being associated with conditions such as depression, anxiety, and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Research in animal models has demonstrated that manipulation of the gut microbiota can lead to changes in behavior and brain chemistry. This has led to a growing interest in the potential use of probiotics and other interventions targeting the gut microbiota to improve brain function and mental health.
While more research is needed to fully understand the complex relationship between the microbiome and brain function, the evidence suggests that our gut microbes can influence our behavior and emotions through their interactions with the brain. This highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy and diverse gut microbiota for overall well-being, including mental health. Evidence suggests that the microbiome can influence stress response, anxiety, and even cognitive function. This has led to the exploration of potential treatments for conditions such as depression and anxiety that target the gut microbiome.
The gut-brain axis, as it is known, is a complex and fascinating area of research that has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of mental health and neurological disorders. It is becoming increasingly clear that the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in brain function and overall well-being.
While the exact mechanisms and pathways involved in this communication are still being explored, the link between the gut microbiome and brain function opens up new possibilities for developing treatments and interventions for a range of mental health conditions. It also highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy and diverse gut microbiome through diet and lifestyle choices.
5. What Makes Our Microbiomes Unique?
Each person's microbiome is as distinctive as a fingerprint. Genetics, diet, lifestyle, and environment all sculpt the composition of our gut microbiota, which in turn can influence our health outcomes. Personalized approaches to health care are beginning to consider this individuality. Additionally, the diversity and specific species of bacteria in our microbiome can vary greatly from person to person. Factors such as age, gender, and geographic location all shape our unique microbiome.
Our microbiomes are constantly changing and evolving based on our daily habits, such as the foods, medications, and even our stress levels. This dynamic nature adds another layer of uniqueness to our individual microbiomes.
Overall, our microbiomes are unique due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that shape the composition and diversity of our gut bacteria. Understanding and appreciating this uniqueness is crucial for personalized health care and disease prevention.
6. How Does Diet Affect Our Microbial Partners?
The foods we consume play a critical role in shaping our microbiome. A diet rich in diverse, fibrous foods supports beneficial microbes, while a diet high in processed foods may encourage harmful pathogens. Probiotics also feature in discussions on reinforcing gut health. Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, provide fuel for beneficial microbes in the gut, promoting their growth and diversity. On the other hand, a diet high in saturated fats and sugars can lead to an imbalance in the microbiome, potentially leading to inflammation and other health issues.
Probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria found in fermented foods and supplements, can also help support a healthy microbial community in the gut. They can help restore the balance of good bacteria and support digestive health.
Overall, a diet rich in a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods can help maintain a healthy and diverse microbiome, which can support overall health and well-being.
7. The Threat of Antibiotics to Microbial Diversity
Antibiotics, while indispensable in our fight against pathogens, concurrently pose a risk to the intricate microbial world that flourishes within our bodies. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have supported the notion that antibiotics, though life-saving, can inadvertently compromise the delicate balance within our microbiota. Their broad-spectrum activity does not discriminate between the harmful invaders and the essential, beneficial bacteria that constitute a healthy microbiome.
The indiscriminate nature of antibiotics can lead to a worrying decline in microbial diversity—the variety of microbial species that inhabit the human gut and other parts of the body. This loss of diversity, research has shown, is not an inconsequential side-effect but a disturbance that can reverberate throughout our health and disease spectrum. For example, changes in the gut microbiota composition have been associated with a heightened susceptibility to conditions ranging from inflammatory bowel disease to obesity and from allergic reactions to mental health challenges. This is mainly due to these microbes' role in fine-tuning our immune system, influencing metabolic processes, and synthesizing crucial nutrients necessary for our well-being.
The microbiome within us continues to evolve, and its composition reflects not only our health status but also a predictor of potential health risks. A healthy microbiome is known to influence brain function, suggesting that the gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters that could affect our mood and cognitive abilities, an area of study that continues to gain traction and holds promises for the future of mental health treatments.
The consequences of dwindling microbial diversity are not restricted to the confines of the human body but extend to the world around us—microorganisms are instrumental in environmental balance, contributing to nutrient recycling and supporting the health of soil and water ecosystems. Researchers have been able to study the genetic material recovered directly from these environmental samples, offering insights into the crucial role these microorganisms play in human health and our planet's ecology.
Strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of antibiotics are becoming a focal point in preserving our microbiota. This includes the necessity for healthcare professionals to prescribe antibiotics, ensuring they are warranted judiciously, and for patients to adhere strictly to their treatment regimens to combat the rise of antibiotic-resistant strains. The scientific community is in pursuit of unraveling the secrets of the microbiome, allowing researchers to explore novel treatments such as phage therapy or precision probiotics that target specific pathogens without destabilizing the overall microbial diversity.
In grasping the significance of our individual's unique microbiome composition, we underline the importance of its role in maintaining the intricate microbial composition in the face of antibiotic challenges. Our health, it seems, is inextricably linked to the countless microbes that reside with us—partners in our journey of life that require care and consideration as much as any other aspect of our well-being.
8. What Can We Learn From Microbiome Research Advancements?
Technological advancements like metagenomic sequencing allow us to analyze the genetic material of microorganisms more thoroughly. This has led to revelations about the role of the microbiome in conditions such as obesity and inflammatory bowel disease, unlocking new avenues for treatment. Additionally, research on the microbiome has shown the importance of maintaining a healthy balance of microbial communities in the gut, which can have far-reaching effects on overall health. Understanding the microbiome can also lead to the development of personalized medicine, as researchers can analyze an individual's microbiome to tailor treatments to their specific microbial makeup.
Microbiome research has highlighted the interconnectedness of human health and the environment, shedding light on how factors such as diet, lifestyle, and exposure to environmental toxins can impact the microbiome and, in turn, improve human health.
Advancements in microbiome research have the potential to revolutionize how we approach and treat various health conditions, leading to more personalized and effective interventions that consider the complex interplay between our bodies and the microbial communities that inhabit them.
9. The Future of Microbiome-Based Therapies
As our understanding grows, so does the potential for innovative therapies. Fecal microbiota transplantation and other microbiome-targeting treatments could revolutionize our approach to health, offering hope for those afflicted by conditions associated with microbial imbalances. One potential future direction for microbiome-based therapies is the development of personalized treatments that take into account an individual's unique microbiome composition. For example, doctors could tailor treatments to address imbalances and promote a healthy microbial community by analyzing the specific bacterial strains in a person's gut.
Genetic engineering and synthetic biology advances could create designer probiotics engineered to deliver specific therapeutic effects. These genetically modified bacteria could be designed to produce certain beneficial compounds or to interact with the host's immune system in a targeted way.
Researchers are exploring the potential of using bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to selectively target and eliminate harmful bacteria in the microbiome while leaving beneficial microbes unharmed. This approach, known as phage therapy, could offer a more precise and personalized alternative to antibiotics for treating bacterial infections.
In cancer treatment, growing interest is in harnessing the microbiome to enhance the body's immune response to tumors. Researchers are investigating how specific gut bacteria may influence the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy, with the hope of developing combination therapies that manipulate the microbiome to improve treatment outcomes.
As with any emerging field, many challenges and unknowns remain to be addressed in developing microbiome-based therapies. However, the rapid pace of research in this area holds great promise for the future of medicine, with the potential to transform the way we prevent and treat a wide range of diseases.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Our Inner Universe
The human microbiome leads with quiet yet pivotal steps in the intricate dance of health and well-being. Though often overlooked, this rich tapestry of microorganisms profoundly shapes our existence, influencing everything from nutrient absorption to mental health. As we peer deeper into this hidden realm, each discovery uncovers new potentials for healing and prevention, beckoning a future where healthcare is as unique as each person's microbiota signature.
Key Points to Reflect On:
- The human microbiome is an integral part of our biology, exerting wide-reaching effects on our health
- The diversity of our microbiota is not just a marker of health but a contributor to it, influencing everything from our immune response to how we process emotions.
- Our diet is a master switch that can alter the microbial populations within us, serving as a tool we can wield to foster a more favorable inner ecosystem.
- Antibiotics, while life-saving, wield the power to disrupt our microbial harmony; their use must be calibrated with precision to avoid unintended consequences.
- Emerging research in microbiome science is unearthing novel ways to approach disease, personalize treatments, and potentially revolutionize our understanding of human health.
As scientists draw back the veil on the complex web of life that thrives within us, we stand on the brink of a new era in medicine—one where the microbiome is not just a participant in our journey to health but a guide. Exploring this microscopic cosmos is a testament to human curiosity and ingenuity. This journey reveals the wonders of the world inside us and reflects how intimately connected we are to the life surrounding us.
References:
- The Hidden World Within Us: Unveiling the Secrets of the Human Microbiome through Bioinformatics - LinkedIn
- The Secret World Inside You - American Museum of Natural History
- Welcome to Your Microbiome: Trillions of Bacteria and Microbes - Amazon.com
- Human Microbiome Featured In The Secret World Inside You - YouTube
- The Human Microbiome: Unveiling the Hidden World Within Us - Course Hero
- Unveiling the hidden world of gut health: Exploring cutting-edge research through visualizing randomized controlled trials on the gut microbiota - PMC
- Unveiling the Secrets of the Microbiome: Exploring the Hidden Universe Within | Education - Vocal.media
- Unveiling the Hidden World of Human Microbiome — Eightify
- Human microbiome the hidden world by agakhanhospital - Issuu
- Human Microbiome: Unveiling Its Profound Significance - The Science Notes
- Healing Secrets: The Wisdom of Your Microbiome with Dr. Zach Bush - Youtube
Hashtags:
#Microbiome #Probiotics #Health #Microorganisms #Microbes #HumanMicrobiome #Genetics #GutHealth #MicrobialDiversity #HealthyLiving #Science #Wellness #GutBrainAxis #ImmuneSystem #PersonalizedMedicine #truehealing